In a recent joint session hosted by TrialAssure and MMS, medical writing professionals from the US and UK gathered to explore one of the most talked-about topics in clinical development today: the real-world application of AI in medical writing. The conversation focused on practical use cases, challenges to navigate, and what the future holds for teams looking to responsibly adopt AI in their workflows.
The Role of AI in Modern Medical Writing
As the complexity of regulatory documentation increases, so does the demand for speed and consistency in medical writing. AI is rapidly becoming an integral part of how teams manage that pressure, offering assistance with everything from content generation and formatting to terminology alignment and data summarization.
However, with about 50 percent of Americans concerned about the increased use of AI, according to Pew Research, more organizations are looking for ways to use AI to decrease timelines, increase profitability, and give time back to their employees.
The core insight from this recent session is AI does not, and should not, replace medical writers. Instead, it should empower them. AI in medical writing has been seen to help reduce repetitive manual tasks and improve document consistency, allowing writers to focus on high-value areas like interpretation, contextualization, and storytelling.
How Organizations Are Adopting AI Today
During the session, several concrete use cases were discussed, particularly around clinical, technical, and plain language documents, like clinical study reports (CSRs) and plain language summaries (PLSs). Based on current work in pharma and biotech, organizations are using AI to:
- Accelerate initial draft document creation
- Maintain consistency across sections and document sets
- Reduce time spent on repetitive edits and formatting
- Support faster review cycles by surfacing inconsistencies or missing elements
Successful implementation begins with pilot programs. These have been shown to provide a controlled way to assess medical writing AI output quality, measure time savings, and build trust within teams. Pilots have also been known to create a natural foundation for change management and cross-functional alignment.
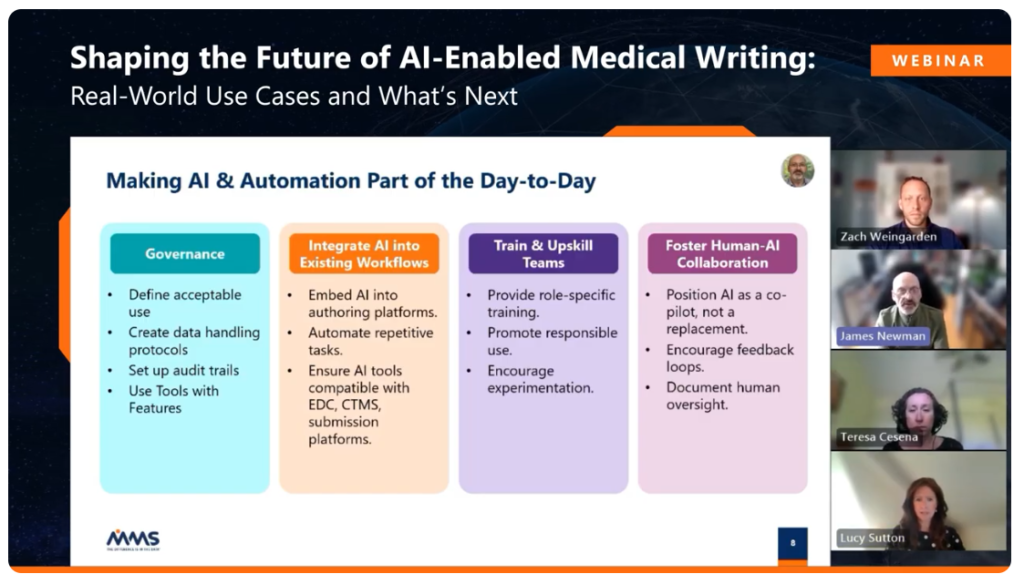
Best Practices for Introducing AI in Writing Workflows
A key theme throughout the discussion was the importance of a human-in-the-loop approach. AI tools are most effective when paired with structured oversight and established writing standards. Based on shared experiences, the following best practices emerged:
- Start with familiar documents. Begin with well-understood formats like PLSs, ICFs, or CSRs to help teams build comfort.
- Create clear prompting strategies. Tailor prompts based on document type and section to guide better AI output.
- Involve experienced reviewers. Human QC is essential to ensure the AI’s suggestions are accurate, relevant, and compliant.
- Track tangible metrics. Log time saved, revisions reduced, or sections completed with AI to measure ROI.
In parallel, organizations should establish a framework for auditability to ensure that all medical writing AI interactions are logged, source data is respected, and regulatory standards are upheld.
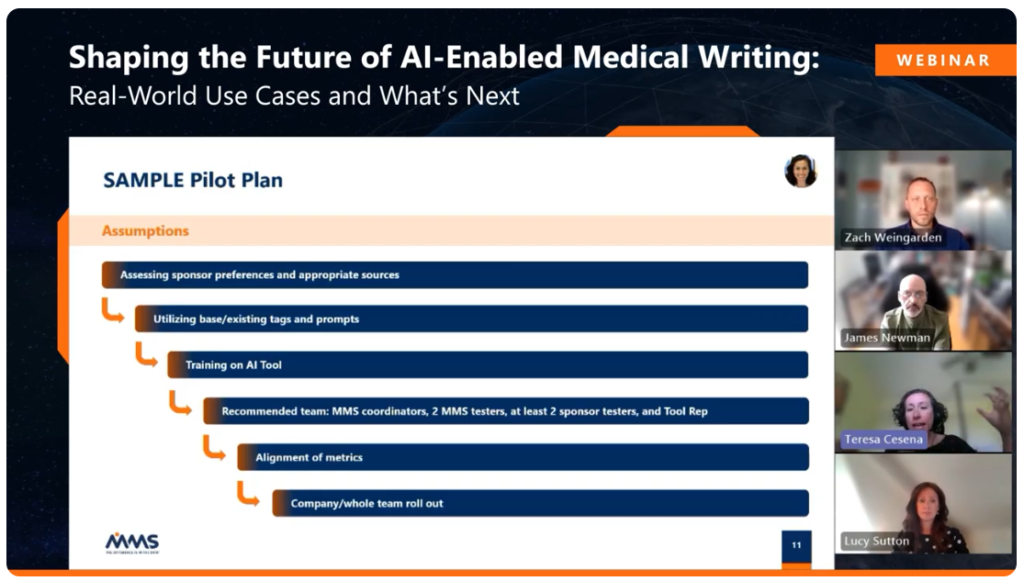
AI’s role in medical writing is expected to expand rapidly in the next few years. Anticipated advancements have the potential to include AI-generated insights across multiple documents, integration of live datasets into AI-assisted authoring, intelligent review suggestions for quality checks, and even tools to support localization, readability, and content tailoring.
Those who invest early in structured, responsible adoption will gain a competitive advantage. Watch the full webinar anytime on demand at https://mmsholdings.com/webinars/ai-medical-writing-webinar/.

